- In March, the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) released the “Human Development Report 2023–2024.” The Human Development Index (HDI) is a summary measure of three basic dimensions: life expectancy, education, and income
- The UNDP has been publishing the indicator since 1990, but the approach was revised in 2010 to take into account changes to the countries surveyed and new calculation methodologies. The latest report covered 193 countries and territories, with Brazil in 89th, two places below its 2021 position (87th). The value of Brazil’s HDI was 0.760 in 2022, slightly higher than it was in 2021 (0.756). Despite this fact, the country fell two places, as the HDI of other countries grew more strongly
- The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the HDI in Brazil and around the world. The graph below demonstrates this impact, showing the sudden change in trajectory in 2019 alongside the projected growth based on pre-pandemic trends.
DATA
How the pandemic affected the HDI
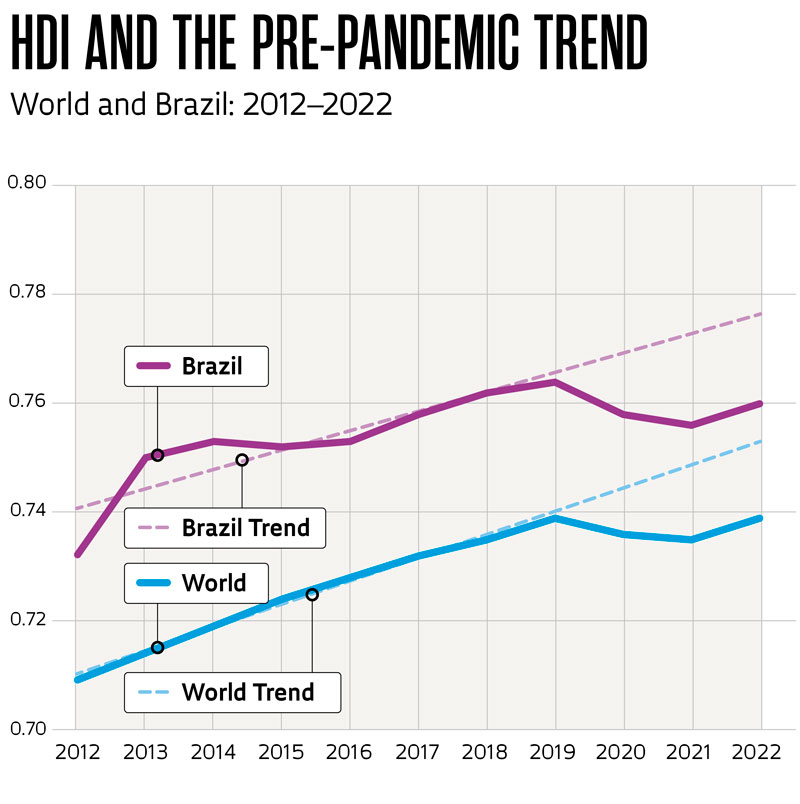
- Compared to projections based on linear regression calculated using 2012–2019 values, today’s global HDI is 1.9% lower than expected, while Brazil’s is at an even lower level: 2.1% lower than its expected value
- Although the 2012–2019 reports do not contain the component values of Brazil’s HDI for the recent period, another report, which detailed HDI on a municipal level (MHDI) in 2021, allows for a deeper analysis of this trajectory, despite its indicators not being fully comparable. The graph below, based on the aggregate national MHDI over time, shows that the pandemic’s greatest negative impact was on life expectancy. Between 2019 and 2021, this specific indicator fell by 4.5%, while those associated with education and income fell by 0.39% and 2.6% respectively

Sources UNDP – Human Development Report 2023–2024; UNDP – MHDI Panel Prepared by the FAPESP, DPCTA, Planning, Studies, and Indicators Team
Republish