- The percentage of young adults (ages 25–34) who completed at least one undergraduate program is one of the most widely used indicators for international comparisons of higher education levels
- According to an OECD survey1, an average of 48% of this population group had completed higher education in 2023 across member countries (see below)
Data
Higher education level among young adults

- Brazil had a rate of 24%2—half the OECD average. This index has been rising over the years and has increased by 8 percentage points since 2013, when it was 15.8%
- Of the other Latin American countries, Peru had the highest rate (50%), followed by Chile (41%), Colombia (35%), Costa Rica (32%), Mexico (28%), and Argentina (19%)
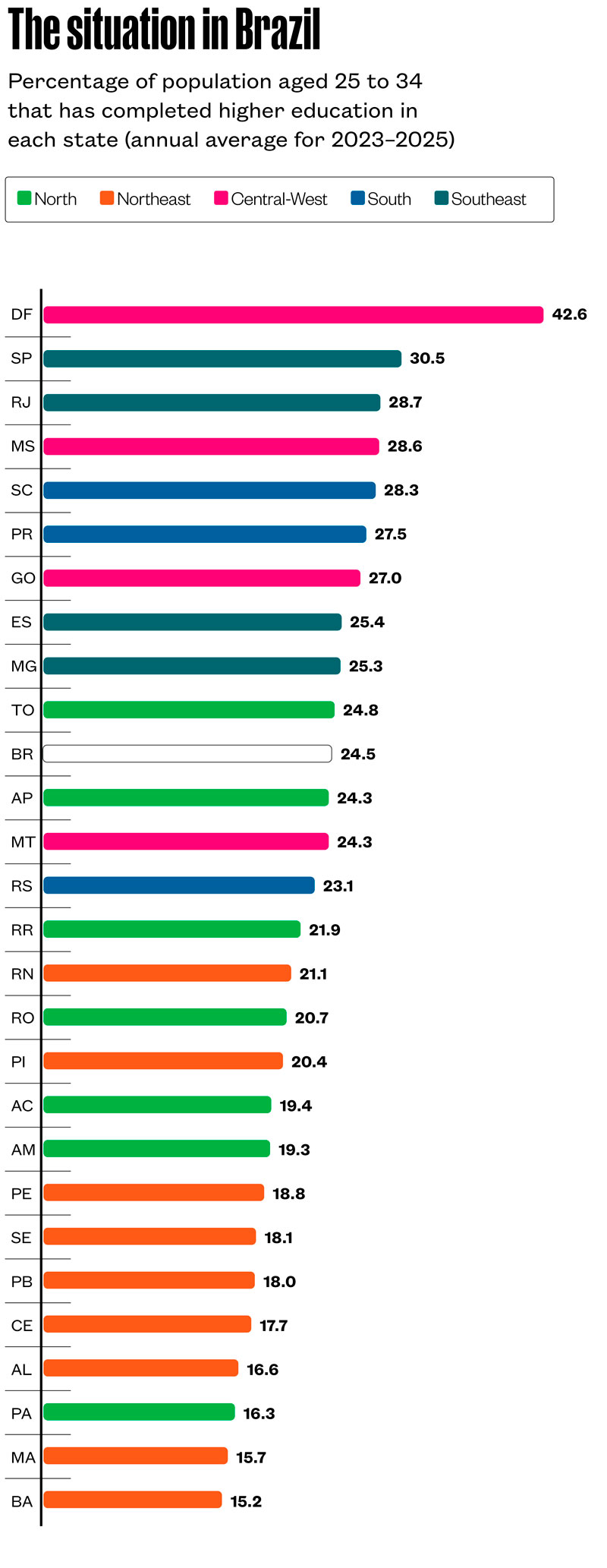
- The variability of the indicator between countries is also seen among the Brazilian states, as shown above, based on the average of the last three years3
- In states of the Southeast region and almost all of the South and Central-West, the rate exceeds the national average, as well as in Tocantins, in the North. The states in the Northeast region are below average
- In Brazil, as in most countries, there are significant differences between the education levels of women and men. For the most recent three-year period, the enrollment rate in higher education among those aged 25 to 34 was 28.2% for women and 20.7% for men
Notes (1) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (2) The exact value is 23.8%. The graph shows rounded values due to the layout (3) The use of a three-year period prevents filtering by state, age, and education from presenting very low numbers in the PNAD-C sample, in some cases
Sources OECD/Data Explorer and IBGE/PNAD-C
Prepared by FAPESP/DPCTA/GPAFI