- Studies of scientific production dynamics indicate that articles written collaboratively by authors from different countries receive more citations
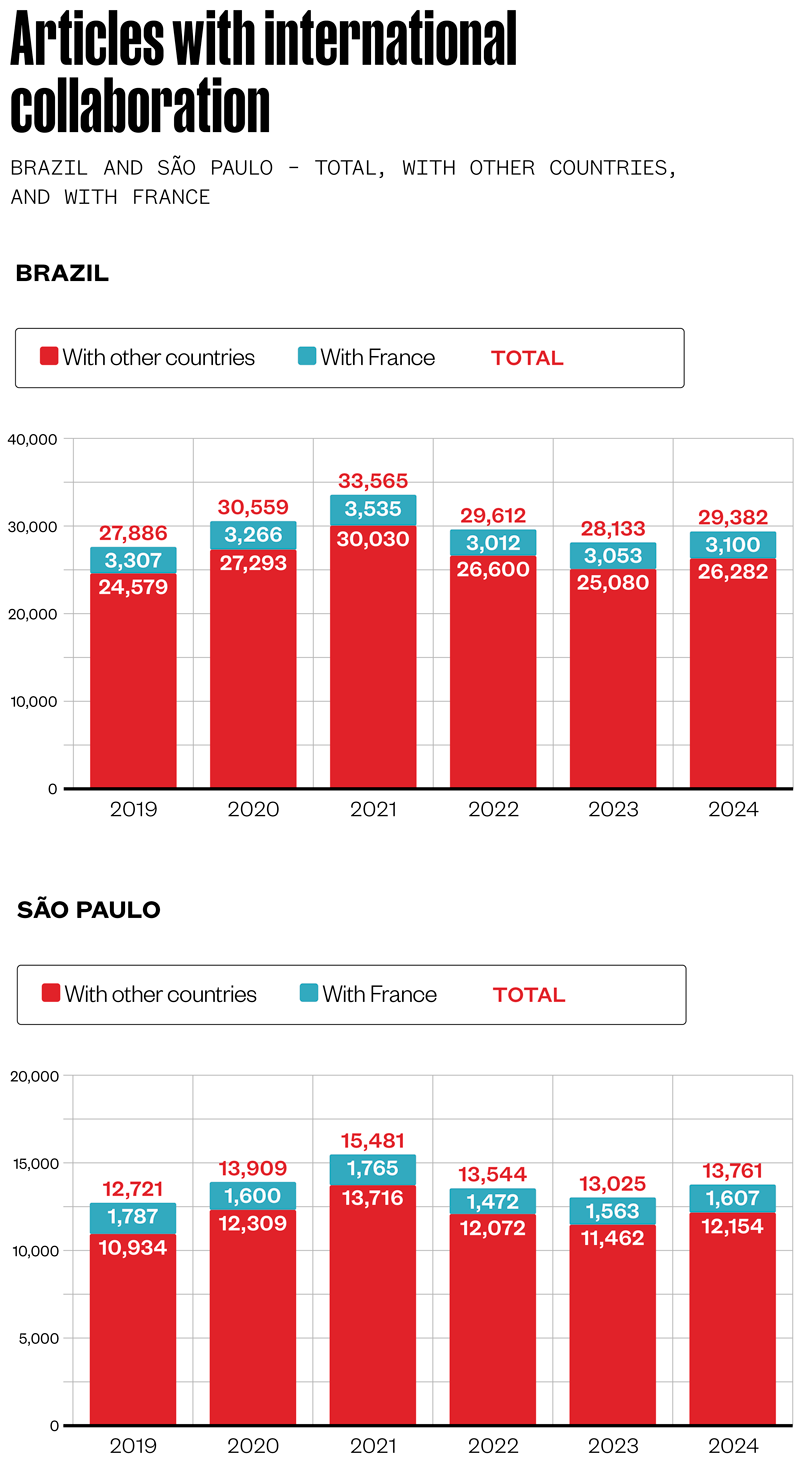
- The graphs below show the numbers of scientific articles1 published by international collaborations2 in Brazil and in São Paulo, with the proportion involving authors from France highlighted. In relative terms, such collaborations are higher in São Paulo than in Brazil over the entire period, at 11.7% and 10.6% respectively in 2024
- The data show that of articles published by Brazilians with international collaboration, 45.6% include authors originally from São Paulo. This figure increases to 51.8% when only considering articles with coauthors residing in France, showing the important role the country plays in São Paulo’s collaborations.
Data
International scientific collaborations with France
- The graph below shows that the number of citations per article3 is much higher when the authors are located in different countries than when all authors are from the publishing country/region
- For articles published in collaboration by Brazil and France, the citation impact was close to 3 in 2023. For collaborations between São Paulo and France, it was between 3 and 4 that year, highlighting the extent to which international collaborations positively influence the citation impact, even for countries with mature research systems, like France

NOTES (1) Published papers indexed by the Web of Science/Clarivate databases as “Articles,” “Proceedings Papers,” and “Reviews.” (2) Published papers with coauthors located in more than one country. (3) The index used is the “Category Normalized Citation Impact” by Clarivate’s InCites platform, which considers the average number of citations per paper for a set of papers, taking into account the year, field, and type of publication, normalized by the world average, given the value of 1.0 (4) Since the number of citations takes time to stabilize, 2024 data should be considered preliminary.
SOURCE Clarivate/InCites
PREPARED BY FAPESP/DPCTA/GIP